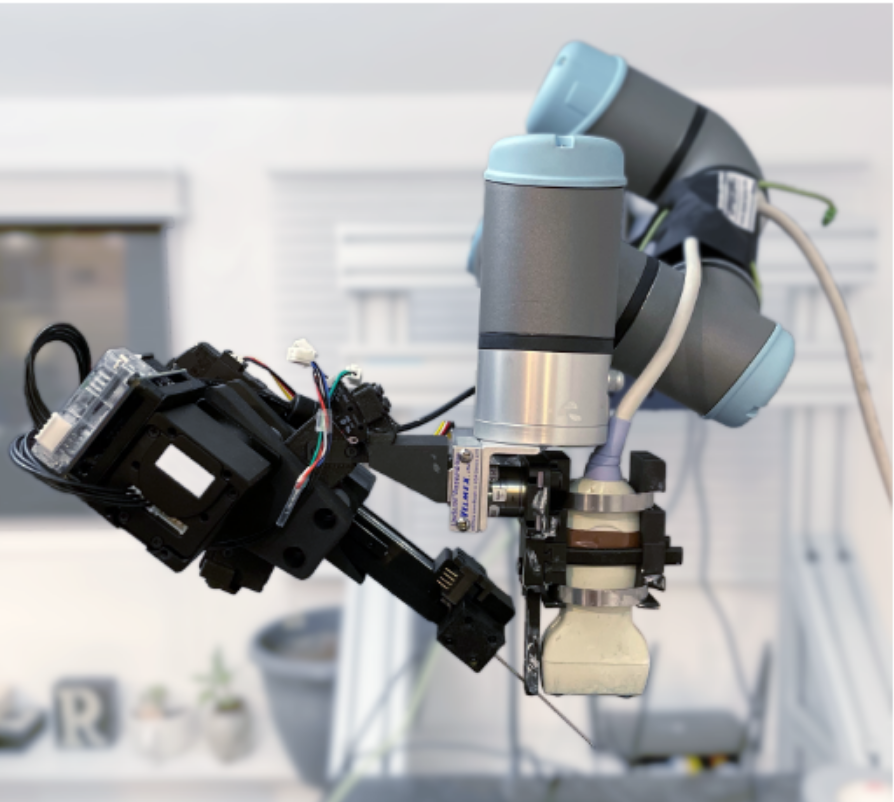
RoboTRAC - Autonomous Vascular Access Robot
Robot to get autonomous vascular access for trauma care in resource-limited settings
Project conducted at the Biorobotics Lab, Carnegie Mellon University, under the guidance of Prof. Howie Choset and Prof. John Galeotti.
Project Abstract
Ensuring timely and effective vascular access is critical for the survival of trauma patients. Vascular access serves as a vital route for delivering anesthesia, resuscitative fluids, diagnostic contrast, and monitoring physiological parameters during primary resuscitation. This is particularly crucial in cases of severe trauma where hemorrhaging is a leading cause of early death, necessitating rapid intervention to replace lost blood volume and treat coagulopathy. Central venous lines play a crucial role in large-volume resuscitation by facilitating the rapid administration of significant quantities of fluids and medications, which may be impractical through peripheral veins. In addition, the integration of robot-guided catheter insertion has the potential to provide essential medical care quickly, especially in situations where medical personnel are not readily available, further emphasizing the importance of timely access to vascular intervention in trauma cases.

Segmentation of Ultrasound Images
In this project, I conducted comparison studies for segmentation of ultrasound images using multiple deep learning frameworks. The frameworks I studied include: 2D U-Net for Image Segmentation, YOLO for Vessel Detection, YOLO + Spokes Ellipse Algorithm for Vessel Segmentation in YOLO detection boxes. To perform these comaprison studies, I curated a dataset consisting of over 14,000 ultrasound images, taken from around 13 porcine experiments. The network performance metric used was IoU score. I compared all these methods for both, single-class segmentation (vessels) and multi-class segmentation (arteries and veins). Here are some of the results that I collected:





References
2023
-
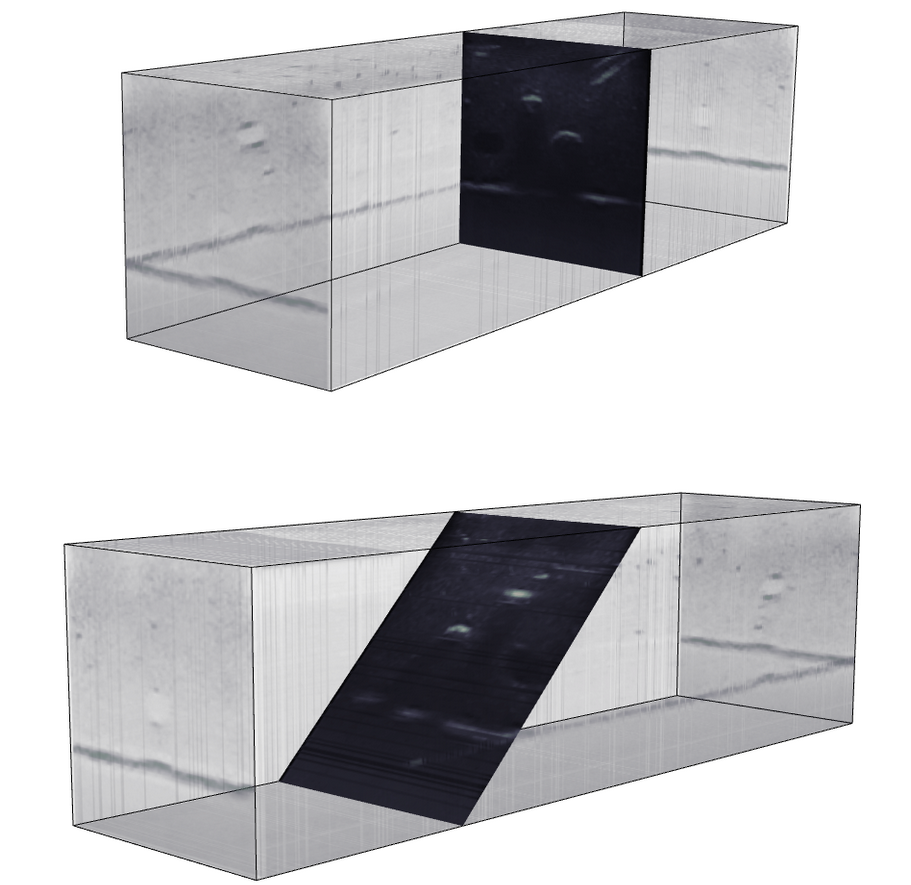 Reslicing Ultrasound Images for Data Augmentation and Vessel ReconstructionIn 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2023
Reslicing Ultrasound Images for Data Augmentation and Vessel ReconstructionIn 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2023